The interaction of groundwater and surface water systems can create mixing zones, particularly in gaining reaches. In these cases, CORMIX may be modified or employed directly to determine the characteristics of these mixing zones. In particular the multiport diffuser options within CORMIX2 may be schematized to account for groundwater recharge source areas in streams and rivers.


Far-Field Flow Processes |
|
|
|
|
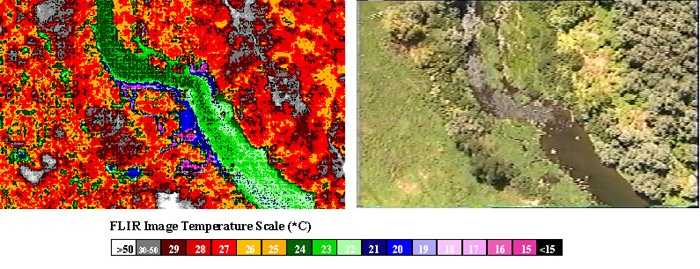
Example of a groundwater-surfacewater interaction mixing zone (Source: Oregon DEQ).
Left image is FLIR data, while right image shows corresponding video. Stream flow is from top to bottom, cool groundwater recharge enters from the
left (river right) below the bend. The subsequent mixing zone shows rapid mixing and suppression of local reach temperature, important for salmonid
habitat analysis and TMDL development.
|
|

This infrared image reveals locations (in yellow) of groundwater seeps into Delaware Bay along Cape Henlopen.
Image: Univ. of Delaware, Sea Grant Reporter, Vol. 19. #1.
|