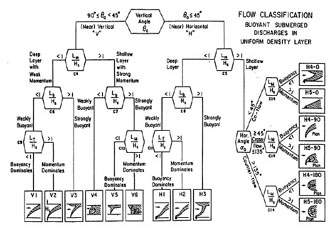
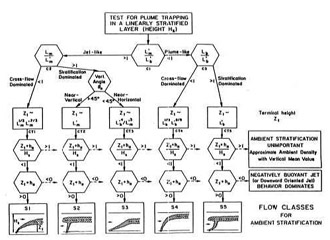
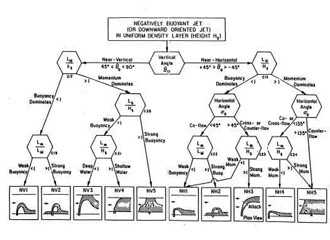
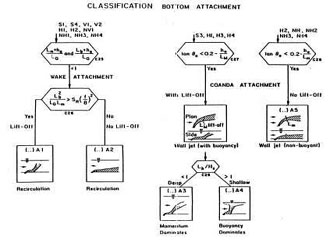
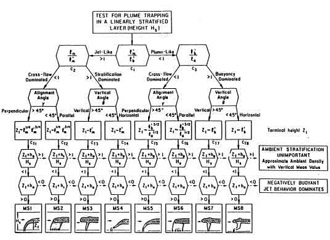
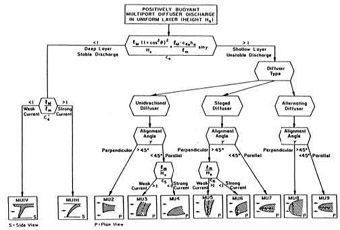
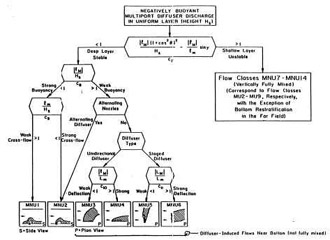
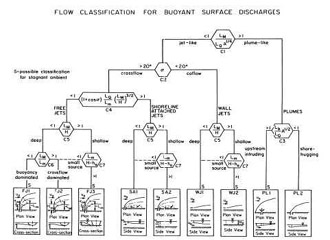
CORMIX contains a rigorous flow classification scheme developed to classify a given discharge/environment interaction and
mixing behvior into one of several flow classes with distinct hydrodynamic features.
The classification scheme places major emphasis on the near-field behavior of the discharge and
uses the length scale concept as a measure of the influence of each potential mixing process.
Flow behavior in the far-field, after boundary interactions, is largely controlled
by ambient conditions.
Once a flow has been classified, integral, length scale, and passive diffusion simulation modeling methods are utilitzed to predict the flow process details.
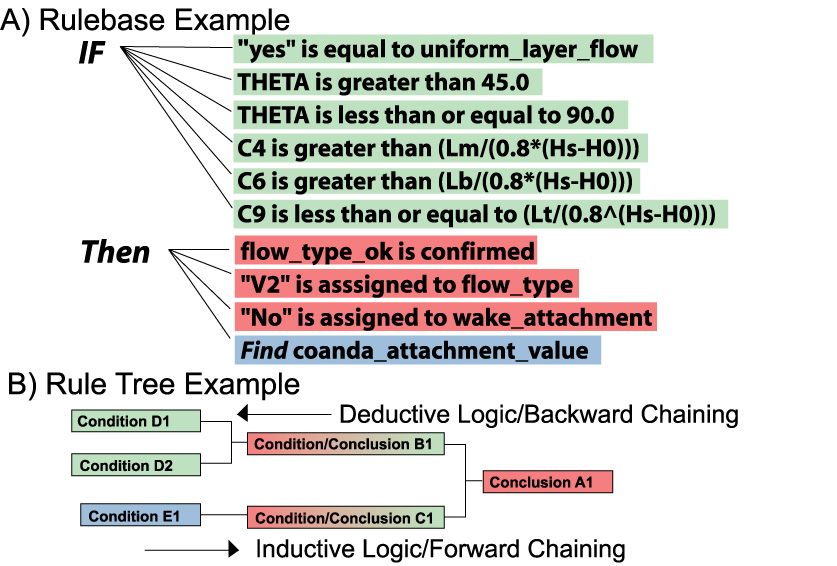
Rule Base Example
Figure on the right illustrates a rule from the Flow Classification Rule Base for determination of CORMIX flow class V2.
A rule base contains a collection of IF(conditions)-THEN(conclusions) logic statements (or rules),
where statements contained within the IF clause are conditions, while statements within the THEN clause
are conclusions or hypotheses. B in the figure above shows that one rule's conditions may themselves be
conclusions of other rules as shown in these rule-tree diagrams.
The system uses both backward (deductive logic) and forward chaining (inductive logic) strategies to reach conclusions about mixing
zone flow behavior, regulatory compliance, and design optimization.
The classification scheme is implemented within CORMIX using Artificial Intelligence (AI)
techniques of rule-based expert systems.
These techniques are used to assist in technology tranfer and to give the analyst flexible and powerful tools for mixing zone
analysis.
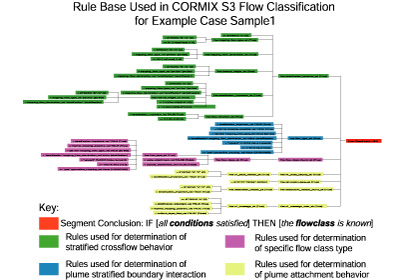
CORMIX rule bases check for input data consistency, calculate basic length scales and flow parameters, determine the flow class, and create the output reports with simulation model details of mixing zone behavior and regulatory compliance. The rule bases also relay conclusions about mixing zone processes to the analyst.
In addition, the classification scheme and rule-base forms a basis for methodical examination of initial mixing properties for environmental impact assessment, regulatory compliance evaluation, ecological impact mitigation and outfall design. Finally, the rule base provides a foundation for outfall design optimization strategies.